
Daily Beast: Just over 97,000 children tested positive for coronavirus in the United States between July 16 and July 30, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics. 338,982 children have tested positive for the virus in total, about 8.8 percent of the total number of cases as of July 30, 3.8 million. (The U.S. surpassed 5 million cases on Sunday.)
How this trump lying about kids getting sick !! YOU CANNOT GO ANY LOWER THAN THAT pic.twitter.com/2QbOEZEts8
— FEW GOOD (@JohnnySargent58) August 8, 2020
In AMERICA due to the REOPENING of schools more than 97000 children tested positive for COVID-19 & R beloved @HRDMinistry
Wants to conduct COMPULSORY EXAMINATION
&@ugc_india vice chairperson @bpatwardhan compares EXAMS WITH LIQUOR STORE@vani_mehrotrahttps://t.co/GxKZeMWI38— FINAL YEAR STUDENT (@FINALYEARSTUD13) August 10, 2020
Children under 18 are less likely develop severe COVID-19 symptoms, but about one third of those who are hospitalized are sent to intensive care, according to a CDC study. The states that had the largest number of pediatric coronavirus cases are California, Florida, Arizona, Tennessee, Illinois, Georgia, North Carolina, and South Carolina, according to the AAP report.
Ainsley Earhardt deals with the consequences of her network & president's covid-19 misinformation: "97,000 kids have tested positive? That was such a shock to me because I had heard kids don't really get it, if they do they're all going to be OK." pic.twitter.com/yKr94fLxcY
— Bobby Lewis (@revrrlewis) August 10, 2020
Children and COVID-19: State-Level Data Report
State-level reports are the best publicly available data on child COVID-19 cases in the United States. The American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association are collaborating to collect and share all publicly available data from states on child COVID-19 cases (definition of “child” case is based on varying age ranges reported across states; see report Appendix for details and links to all data sources).
On July 30, the age distribution of reported COVID-19 cases was provided on the health department websites of 49 states, New York City, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and Guam. While children represented only 8.8% of all cases in states reporting cases by age, over 338,000 children have tested positive for COVID-19 since the onset of the pandemic.
A smaller subset of states reported on hospitalizations and mortality by age, but the available data indicated that COVID-19-associated hospitalization and death is uncommon in children.
At this time, it appears that severe illness due to COVID-19 is rare among children. However, states should continue to provide detailed reports on COVID-19 cases, testing, hospitalizations, and mortality by age so that the effects of COVID-19 on children’s health can continue to be documented and monitored.
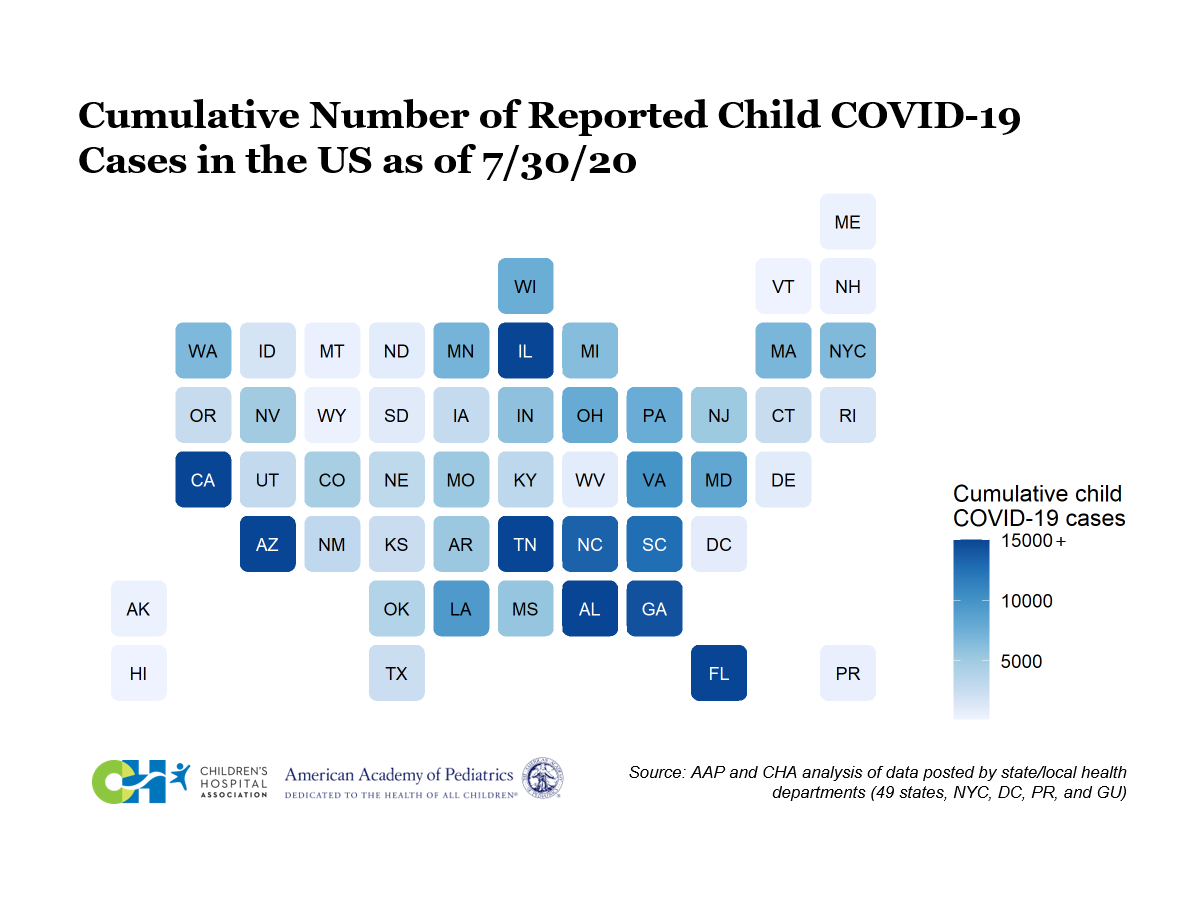
Summary of Findings Reported on 7/30/20:
(Note: Data represent cumulative counts since states began reporting)
Cumulative Number of Child COVID-19 Cases*
- 338,982 total child COVID-19 cases reported, and children represented 8.8% (338,982/3,835,573) of all cases
- Overall rate: 447 cases per 100,000 children in the population
Change in Child COVID-19 Cases, 7/16/20 – 7/30/20
- 97,078 new child cases reported from 7/16-7/30 (241,904 to 338,982), a 40% increase in child cases
Testing (8 states reported)*
- Children made up between 3%-11.3% of total state tests, and between 3.6%-18.4% of children tested were tested positive
Hospitalizations (20 states and NYC reported)*
- Children were 0.6%-3.7% of total reported hospitalizations, and between 0.6%-8.9% of all child COVID-19 cases resulted in hospitalization
Mortality (43 states and NYC reported)*
- Children were 0%-0.8% of all COVID-19 deaths, and 20 states reported zero child deaths
- In states reporting, 0%-0.3% of all child COVID-19 cases resulted in death
*Note: Data represent cumulative counts since states began reporting
Additional Information
- AAP News COVID-19 Collection
- Latest message from AAP President Sally Goza, MD, FAAP
- Red Book Online Outbreaks page
- Pediatrics COVID-19 Collection
ATTENTION READERS
We See The World From All Sides and Want YOU To Be Fully InformedIn fact, intentional disinformation is a disgraceful scourge in media today. So to assuage any possible errant incorrect information posted herein, we strongly encourage you to seek corroboration from other non-VT sources before forming an educated opinion.
About VT - Policies & Disclosures - Comment Policy



